Knee Replacement Surgery
Are you considering knee replacement surgery? A knee replacement surgery or knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint to relieve pain and disability.
Pain resulting from an injured or diseased knee can severely limit your daily activities and ability to move or work.
A knee replacement procedure is most commonly performed on patients with osteoarthritis, and also for other knee diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
In patients with severe deformity from advanced rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, or long-standing osteoarthritis, the surgery may be more complicated and may carry higher risk.
Osteoporosis does not typically cause knee pain, deformity, or inflammation and is not a reason to perform knee replacement.
The knee joint is the largest joint in your body and it is central to nearly every routine activity.
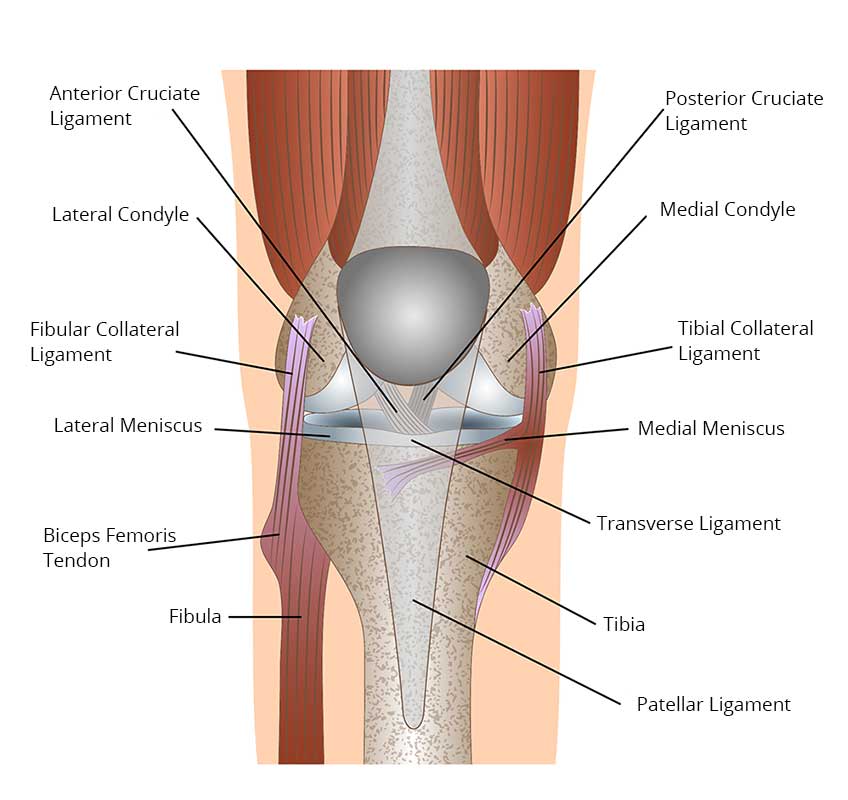
The knee joint is formed by the ends of three bones.
- The Femur or lower end of the thigh bone.
- The Tibia or upper end of the shin bone.
- And the Patella or kneecap.
The ligaments connect the knee bones and stabilize the knee joint. The cartilage covers the end of the knee bones and prevents them from rubbing against each other, allowing for flexible and almost frictionless movement.
Other major causes of debilitating pain include meniscus tears, cartilage defects, and ligament tears. Debilitating pain from osteoarthritis is much more common in the elderly.
Knee replacement surgery can be performed as a partial or a total knee replacement. A knee replacement surgery consists of replacing the diseased or damaged joint surfaces of the knee with metal and plastic components shaped to allow continued motion of the knee.
The procedure typically involves substantial postoperative pain, and includes vigorous physical rehabilitation. The recovery period may be 6 weeks or longer and may involve the use of mobility aids (e.g. walking frames, canes, crutches) to enable the patient's return to preoperative mobility. It is estimated that approximately 82% of total knee replacements will last 25 years.
Knee replacement surgery is recommended:
- If you had a previous knee injury, torn ligaments or a broken bone around the knee sometimes will result in arthritis that causes great pain and limits your movement.
- If you are suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, which attacks your body’s immune system and destroys the lining of the knee.
- If you suffer from deformities, patients with bowed legs or knock-knees often get surgery to restore the overall position of the knee.
- If you find yourself in constant knee pain. You are not able to move like you used to.
- It is painful to climb stairs, walk the dog, or simply get up from bed or out of a chair.
- If you have tried medicines, injections, and physical therapy and nothing seems to work.
- If that is what you are experiencing, it may be time to consider knee replacement surgery.
About Knee Replacement Surgery Options
Stryker® Mako™ Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Replacement
Stryker® Mako™ Robotic-Arm Assisted Partial Knee Replacement
Traditional Knee Replacement
Non-Muscle Cutting Knee Replacement
Tourniquet-Less Knee Replacement
Dr. Ronald Hudanich is a board-certified orthopedic surgeon and has a long history of successfully treating patients with knee, hip, and shoulder degenerations and joint replacement surgeries. Dr. Hudanich is specially trained to restore your range of motion, ease the pain, and enable you to regain your active lifestyle with a partial, total or revised joint replacement surgical option that is best for you.
For additional questions please call us at (407) 977-4130 or visit American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.